
5
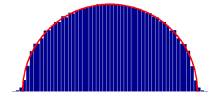
Wigner’s Semi-Circle
vThe
classical & most famous rand eig theorem
vLet S =
random symmetric Gaussian
vMATLAB:
A=randn(n); S=(A+A’)/2;
vNormalized
eigenvalue histogram is a semi-circle
vPrecise
statements require n®¥
etc.